Collected Problems for Test 2
Problem #7(Due 2/17 Monday by 9:00 a.m.)
a) A charge moves along the +x axis and experiences no magnetic force, although there is a magnetic field. What can you conclude about the direction of the magnetic field? Explain
b) A moving charge experiences the maximum possible magnetic force when moving in a magnetic field. What can you conclude about the angle that the charge's velocity makes with respect to the magnetic field? Explain
c) A particle that has a 8.2 microcoulomb charge moves with a velocity of magnitude 5.0 x 105 m/s. When the velocity points along the +x axis, the particle experiences no magnetic force, although there is a magnetic field present. The maximum possible magnetic force that the charge could experience has a magnitude of 0.68 N. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field. Note that there are two possible answers for the direction of the field. Make sure you draw a diagrams indicating charges, velocities, forces, and magnetic fields.
Problem #8 (Due 2/19 Wednesday by 9:00 a.m.)
a) You have a wire of length L from which to make the square coil of a dc motor. In a given magnetic field a coil of N turns each with area A produces more torque when its total effective area of NA is greater rather than smaller. Is more torque obtained by using the length of wire to make a single-turn coil or a two-turn coil? Explain.
b)The length of the wire is L = 1.10 m. The current in the coil is I = 1.7 A, and the magnetic field of the motor is 0.34 T. Find the maximum torque when the wire is used to make a single-turn square coil and a two-turn square coil. Verify that your answers are consistent with your answer to part a.
Problem #9 (Due 2/21 Friday by 9:00 a.m.)
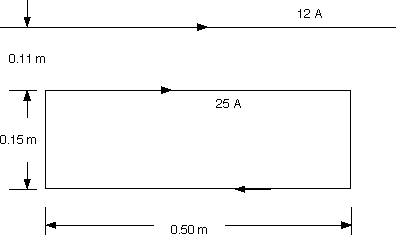
A rectangular current loop is located near a long, straight wire that carries a current of 12 A. The current in the loop is 25 A. Determine the magnitude of the net magnetic force that acts on the loop.

Problem #10 (Due 2/25 Tuesday by 9:00 a.m.)
10a.
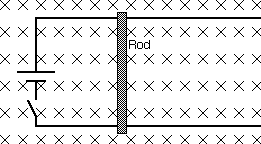
A conducting rod is free to slide along a pair of conducting rails, in a region where a uniform and constant (in time) magnetic field is directed into the plane of the paper (screen), as the drawing illustrates. Initially the rod is at rest.
a) When the switch is closed what is the direction of the current?
b) Is there a force on the rod? In which direction is it? Explain.
c) Describe the rod's motion after the switch has been closed for a while. Explain.
10b. A house has a floor area of 112 m2 and an outside wall that has an area of 28m2. The earth's magnetic field here has a horizontal component of 2.6 x 10-5 T that points due north and a vertical component of 4.2 x 10-5 T that points straight down, toward the earth. Determine the magnetic flux through the wall if the wall faces a) north and b) east. c) Calculate the magnetic flux that passes through the floor.
Problem #11 (Due 2/28 Friday by 9:00 a.m.)
The rechargeable batteries for a laptop computer need a much smaller voltage than what a wall socket provides. Therefore, a transformer is plugged into the wall socket and produces the necessary voltage for charging the batteries.
a) Is the transformer a step-up or a step-down transformer? Explain.
b) Is the current that goes through the batteries greater than, equal to, or smaller than the current coming from the wall socket? Explain.
c) If the transformer has a negligible resistance, is the electrical power delivered to the batteries greater than, equal to, or less than the power coming from the wall socket? Explain.
d) The batteries of a laptop computer are rated at 9.0 V, and a current of 225 mA is used to charge them. The wall socket provides a voltage of 120 V. Determine the ratio of turns of the primary coil to the secondary coil for this transformer.
e) What is the current coming from the wall socket?
f) Find the power delivered by the wall socket and the power sent to the batteries.