A light beam enters the prism below. The prism is surrounded by air. If the light beam strikes surface 2 at the critical angle what is ![]() ?
?
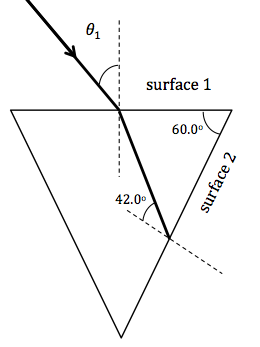
Ans. 27.5o
Problem 4
A converging lens of focal length f1=11.0 cm is placed 52.0 cm to the left of a converging lens of focal length f2 = 22.0 cm. When an object is placed to the left of lens 1 the lens combination forms a final image 33.0 cm to the right of lens 1 (so the final image is between the lenses).
a. Sketch the
set up in a diagram (don't solve graphically, just draw the set up).
b. How far to the left of lens 1 is the object positioned?
c. What is the overall magnification of the lens combination?
d. Is the final image upright or inverted?
Ans. b. 14.9 cm, c. -5.22m d. inverted
Problem 5
Two slits with a sparation of 8.5 x 10-5 m create an interference pattern on a screen 2.3 m away. If the tenth bright fringe above the central fringe is a linear distance of 12 cm from it, what is the wavelength of light used in the experiment?
Ans. 440 nm
Problem 6
A thin film of magnesium fluoride (n = 1.38) is coated on a glass camera lens (n = 1.5). The thickness of the film is 1.01 x 10-5 cm.
a. Sketch a picture showing any phase changes.
b. Find any wavelengths in the visible spectrum that are intensified in the reflected light?
Ans. There are none
Problem 7
For a wavelength of 420 nm, a diffraction grating produces a bight
fringe at an angle of 26o. For an unknown wavelength, the same
grating produces a bright fringe at an angle of 41o. In both cases
the bright fringes are of the same order m. What is the unknown
wavelength?
Ans. 630 nm