Problem Set #5
#1. A 30.0 g arrow is shot by William Tell through an 8.00 cm thick apple sitting on top of his son's head. The arrow enters the apple at 30.0 m/s and emerges at 25.0 m/s in the same direction.
a) Sketch a free body diagram of the arrow when passing through the apple.
b) What is the acceleration of the arrow?
c) With what force has the apple resisted the arrow?
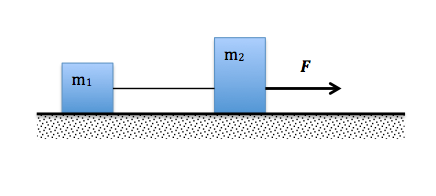
#2. Two boxes are connected by a light rope are on a frictionless surface. A force F is applied to m2 causing the masses to accelerate at 2.43 m/s2 to the right. The mass of m1is 4.11 kg and the mass of m2 is 6.21 kg.
a) Draw a free body diagram of each block.
b) What is the tension T in the connecting rope?
c) What is F?

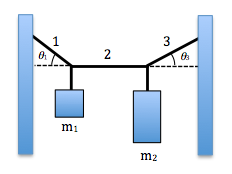
#3. The diagram below shows a mass m1 = 2.1 kg and a mass m2 = 4.1 kg suspended from lightweight cables. It is found that theta 1 is equal to 20o when the center rope is adjusted to be closely horizontal. Determine the tension and the angle of rope 3.
#4. A winch is used to drag a 375 N crate up a ramp at a constant speed of 75 cm/s by means of a rope that pulls parallel to the surface of the ramp. The rope slopes upward at 33o above the horizontal, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ramp and the crate is 0.25.
a) Draw a free body diagram.
b) What is the tension in the rope.
c) If the rope were suddenly to snap, what would be the acceleration of the crate immediately after the rope broke? Draw a new free body diagram.
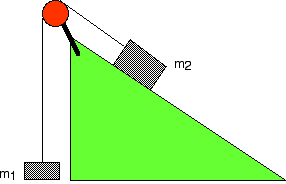
#5. Objects of masses m1=4.00 kg and m2 = 9.00 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. The object m1 is held at rest on the floor, and m2 rest on a fixed incline of 40.0o relative to the horizontal. The objects are released from rest, and m2 slides 1.00 m down the incline in 4.00s.
a) Determine the acceleration of the object.
b) Find the tension in the string.
c) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between m2 and the incline?