EE
2212
PROBLEM
SET 6
S.
G. Burns
Due: Wednesday, 6 March 2013
1. Your smart phone requires 9.0
VDC regulated with a receive current of 5 mA and a
transmit current of 200 mA. You want to use your
car’s power port which has a nominal and lowest output voltage of 12 VDC
although the voltage could go as high as 14.4 VDC when the engine and
alternator are running. Design an
avalanche diode (Zener diode) voltage regulator that
will allow you to operate your smart phone from the power port. Use the
discussion and circuit diagram discussed in class as well as Problem 4 on Problem
Set 5 for guidance. (Of course you
wouldn’t use your smart phone while you were driving!)
Your design
should include:
(a)
A well-labeled schematic diagram
(b)
Key design equations
(c)
Values including power ratings for any
resistor(s) needed.
(d)
Avalanche diode specifications that would
work including VZ, IZ(min),
IZ(max) and PZ.
2. A power diode is rated at Imax = 6 A
and VJ = 0.7 volts. The case
temperature is not to exceed TC = 150°C. The thermal resistance θJC
= 4.25°C/W.
(a)
Estimate the junction temperature at maximum
case temperature.
(b)
If the ambient temperature is TA
= 30°C, what is the maximum thermal resistance, θCA,
of the heat sink?
3. Even though there are no assigned problems
related to our discussions about photonic concepts and devices from 27 February
and 1March, you should understand the content and interpretation
of the information given in posted WEB
pages SolarConstantInformation.docx SolarPanel1.JPG Poster.ppt
Note 1: We
will be starting Chapter 4 “Field-Effect Transistors” on Monday, 4 March. Problems 4 and 5 are plug-and-chug to get you familiar
with units and nomenclature.
Note 2: First observe that in lieu of specifications
not explicitly stated in any given problem assigned in Chapter 4, the general
specifications in Table 4.6 on page 204 are to be used. Other
important numbers are also listed below Table 4.6.
4. Text Problems 4.1 and 4.2 and for 4.2, observe that this is
Cox, capacitance per unit area. Watch
your units. Usually capacitance/cm2
are preferred for the area reference. When the text and in the industry talks about
an MOS capacitor, they are usually referring to capacitance/unit area. The total capacitance can then be scaled by
the W x L product. The parallel plate
basic capacitor model works well!
5. Text 4.4 and 4.8 for NMOS and Text 4.48 for PMOS. Organize your results in a table.
Recall
the WOM (Write-Only-Memory) Signetics Data Sheet from the attachment to the
diode experiment, Experiment 4. I think
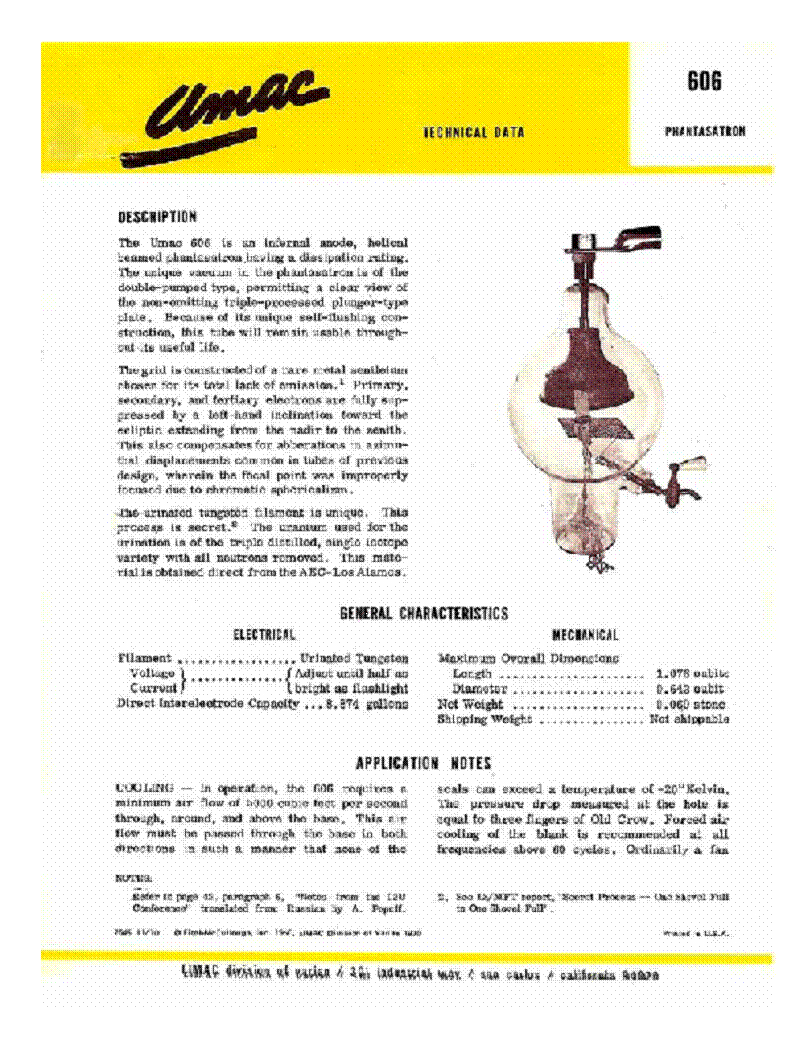
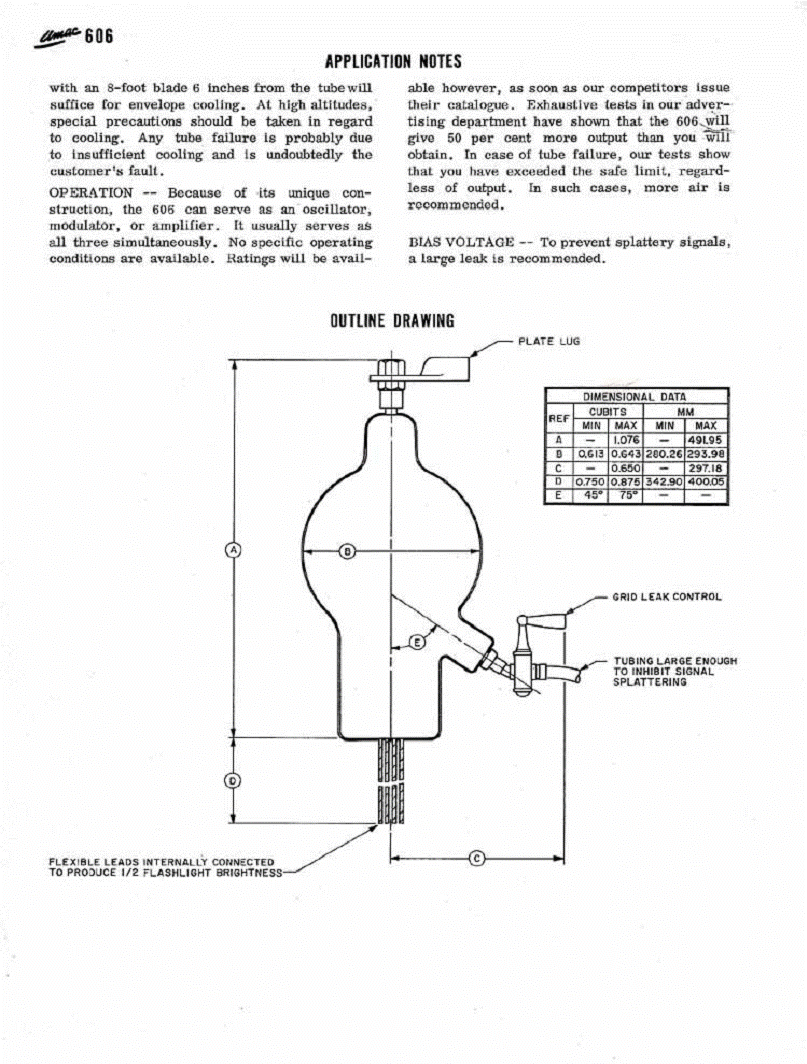
those engineers may have taken a clue from some engineers at EIMAC. The EIMAC division manufactures high power
and specialty vacuum tubes used in high power transmitters and RF generators
and related. This is a data sheet for the “PHANTASATRON”. EIMAC is now a subsidiary
of Communications and Power Industries.
Enjoy!