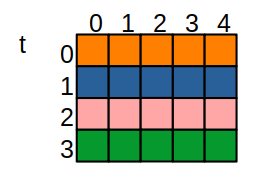
Consider the 2D array declaration:
int t[4][5];
We can visualize t as:

However, the elements of t are laid out in memory as:
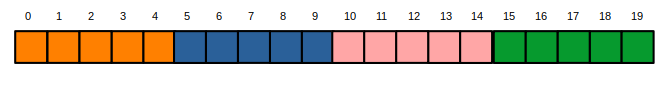
In general, if a 2D array t
has row size r, then the location in memory of the element
referenced by t[i][j] is calculated by:
i * r + j
For example:
t[0][0] → 0 * 5 + 0 = 0
t[2][2] → 2 * 5 + 2 = 12
t[3][4] → 3 * 5 + 4 = 19