Basic Terms and Concepts
in American Archaeology
After Willey, Gordon Randolph, and
Philip Phillips, Method and Theory in American Archaeology.
(Chicago: University of Chicago Press 1970, 1958.)
- the smallest unit of space dealt with by the archaeologists
- most difficult to define
(2) locality
- is the archaeological parallel of a single community
- slightly larger spatial unit than the site
- varies in size from a single site to a district of uncertain
dimensions
- but is generally not larger than the space that might
be occupied by a single community or local group
- strictly is a geographical space small enough to permit
the working assumption of complete cultural homogeneity at any given
time
- "a considerably larger unity of geographical space
usually determined by the vagaries of archaeological history"
- environmental considerations are important
(4) area
- Mesoamerica
- defined by Paul Kirchoff in 1952
- Other American "Areas"
- Southwest (U.S.A.)
- Southeast (U.S.A.)
- Amazonia
- Chibcha (Circum-Caribbean)
- Andean (Peru)
- natural environments and cultural regions of Mesoamerica
(slides)
Temporal Series (2)
(1) local sequence [locality]
- In the Central Highland Valley of Mexico there are at least
five major local sequences
(2) regional sequence [region]
- not merely a local sequence with larger spatial dimensions
- the Central Highland Valley of Mexico
- regional sequence would correlate the above local
sequences
- regional sequences are the result of correlating
the local sequences, not combining them
- asks questions of wider relationships
Integrative Units (3)
- deal with the problem of large-scale integration
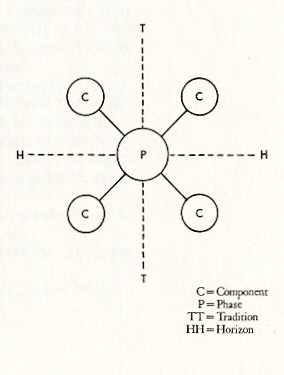
(1) tradition
- is a primarily temporal continuity represented by persistent
configurations in single technologies or other systems of related
form
- stable geographical boundaries are implies
- in sum, the tradition gives depth, while the horizon gives
breadth
(2) horizon
- a primarily spatial continuity represented by cultural
traits and assemblages whose nature and lode of occurrence permit
the assumption of broad and rapid spread
- the archaeologically unites linked by a horizon are assumed
to be approximately contemporaneous
- in sum, the horizon gives breadth, while the tradition
gived depth
- "horizon style"
- occupies a great deal of space but little time
- may roughly be defined as a specialized cultural continuum
represented by the wide distribution of a recognizatble art
style
(3) climax
- not often used, but includes the type or types of maximum
intensity and individuality of an archaeological horizon or tradition
- is necessarily a value judgment, but only in terms
of the horizon or tradition involved
- in whole cultural terms the climax becomes the phase
or phases of maximum intensity and individuality of a culture
or civilization
Basic Archaeological Units (2)
- "form" or "content" units
- i.e., the element of content is more important
in their formulation than the spatial and temporal dimensions
Process
- how things develop or change over time
- a series of occurrences and events that produce change or development
- "How did X get to be this way?"
- examples
- domestication of maize
- rise and fall of civilizations and/or parts thereof
- the "agricultural revolution"
- the development of a market economy
- the invention of pottery and advanced ceramic techniques and technologies
Stages

(handout)
|


